What is K3s? A Deep Dive into Its Architecture and Philosophy#
K3s is a fully supported Kubernetes distribution, but with a much smaller memory footprint and installation size than its K8s counterpart. It is distinguished by being packaged as a single binary of less than 100 MB, making it easy to install and deploy. This feature is crucial to its versatility, allowing it to be used in scenarios ranging from edge computing to local development environments.
K3s was created by Rancher, with the goal of providing a Kubernetes solution that was easy to manage, even for those without extensive cluster management experience. The phrase “situations where a K8s clusterology PhD is unfeasible” perfectly sums up this philosophy: K3s seeks to remove the barriers to entry to Kubernetes, allowing more developers and organizations to take advantage of its potential.
Key Use Cases#
The versatility of K3s makes it an attractive option for a wide range of applications:
- Edge Computing: Deploy applications on devices close to the data source, reducing latency and improving real-time performance. This is crucial for IoT applications, real-time video analytics and industrial control systems.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Manage applications on resource-constrained devices, from sensors to smart home devices. K3s allows to deploy and update applications remotely on these devices in an efficient way.
- Home Labs (Homelab): Provides a simple and efficient way to experiment with Kubernetes without the overhead of a full cluster, ideal for students, enthusiasts and developers looking to learn and experiment with this technology.
- Continuous Integration (CI): Provides a consistent environment for testing and development, accelerating the software lifecycle. K3s allows to create test environments quickly and easily, facilitating the early detection of errors.
- Local Development: Allows developers to work with Kubernetes locally and easily, without the need for complex infrastructure. This streamlines the development and testing of container-based applications.
- ARM Devices and Single-Circuit Boards: Fully compatible with ARM architectures, such as Raspberry Pi, opening up a world of possibilities for electronics and robotics projects.
- Air-gapped environments: Works in environments without internet connection, ideal for high security situations where network access is limited or non-existent.
- Embedded Systems: Easily integrates with other applications and systems, enabling management of containerized applications in a variety of contexts.
Technical Features: Breaking Down the Power of K3s#
Minimalist Design and Architecture#
- K3s is distributed as a single executable binary or minimal container image, which greatly simplifies installation and management. This feature reduces deployment complexity and facilitates automation.
- Lightweight Datastore: Uses sqlite3 as the default data storage, ideal for low-demand environments. However, for larger clusters or for those requiring greater resiliency, also supports etcd3, MySQL and Postgres.
- Simplified Launcher: Incorporates a launcher that manages the complexity of TLS (Transport Layer Security) and other configuration options, automating many of the configuration tasks that in traditional Kubernetes would be manual.
- Encapsulated Components: All components of the Kubernetes control plane (API Server, Scheduler, Controller Manager) are encapsulated in a single process, simplifying operation and automating tasks such as certificate distribution. This reduces resource overhead and improves stability.
Key Benefits#
- Default Security: Comes configured with secure defaults for lightweight environments, minimizing the risk of vulnerabilities and simplifying the security configuration.
- Minimal Dependencies: Requires a modern kernel and cgroup mounts, reducing the need for external dependencies and facilitating deployment on different operating systems.
- “Included Batteries”: K3s includes all necessary dependencies for easy cluster creation:
- containerd/cri-dockerd: Container Runtime.
- Flannel: Container Network Interface (CNI).
- CoreDNS: Cluster DNS.
- Traefik: Ingress Controller.
- ServiceLB: Load Balancing Controller.
- Kube-router: Network policy controller.
- local-path-provisioner: Persistent volume controller.
- Spegel: Distributed container image registration mirror.
- Host utilities:
iptables,socat, among others.
- Resource efficiency: K3s uses half the memory of K8s, making it ideal for resource-constrained environments.
Comparison with Kubernetes (K8s)#
While K3s shares the core of Kubernetes, there are important differences:
| Feature | Kubernetes (K8s) | K3s |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Large, multiple components | Small, single binary less than 100MB |
| Complexity | High, multiple components and configurations | Low, simple configuration, ideal for beginners and resource constrained environments |
| Memory Usage | High | Low, uses half the memory of K8s |
| Database | Generally etcd, distributed and complex | sqlite3 by default, with support for etcd3, MySQL and Postgres for scalability |
| Ideal for | Large deployments, high availability, complex environments and mission-critical applications | Edge environments, IoT, local development, home labs, testing, resource-constrained devices |
| Scalability | High | Moderate, but can be used for distributed systems with the right database |
| Distributed Database | Natively included | Not natively included, Rancher’s Dqlite solution should be used if distributed database is desired |
The Name K3s: An Acronym with a History#
The name “K3s” is an homage to Kubernetes (K8s), where the “K” is the first letter and the numbers “8” and “3” represent the number of letters remaining in each name. It was chosen to indicate that it is a smaller version, about half the size in terms of memory footprint. It has no official long form or official pronunciation.
Why Choose K3s? Concrete Benefits#
K3s is an ideal choice if you are looking for a Kubernetes solution that is:
- Easy to install and configure: Single command installation simplifies the process.
- Low resource consumption: Uses half the memory of K8s, ideal for hardware-constrained environments.
- Fast to deploy: Reduces deployment times, speeding up development and testing cycles.
- Ideal for experimentation and prototyping: Allows developers and enthusiasts to dive into the world of Kubernetes without hassle.
- Perfect for Edge Computing: Provides a robust, lightweight solution for running applications on devices at the edge of the network.
- Suitable for IoT: Facilitates application management on resource-constrained devices.
Installation and Setup Step-by-Step
K3s installation is incredibly simple, allowing anyone to get started with Kubernetes quickly.
K3s or K3D Installation#
Installation of K3S (Linux):#
curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | sh -
This command downloads and installs K3s on the system. The process is fast and automated.
K3D Installation (macOS):#
If you tried to install it on macOS with the above command, you will receive an error message like the following: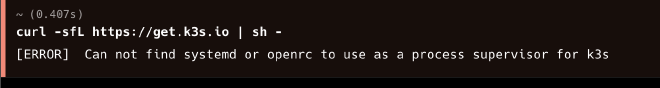
This is because you need to use systemd/OpenRC, which should be as an extra Linux layer on macOS and it is not, so it is a problem, and here comes K3D to the rescue.
To run it, we need to have previously installed Docker Desktop as well as brew on our mac, and run the following command:
brew install k3d
This command downloads and installs K3D on the system using Docker containers. The process is fast and automated.
Creating our first cluster.#
To create our first cluster using K3S/K3Ds with default values, we must execute one of the following commands:
Using K3S (Linux)#
| |
Using K3D (macOS)#
| |
Once you run the correct version for your operating system, you will see in your console something like the image below: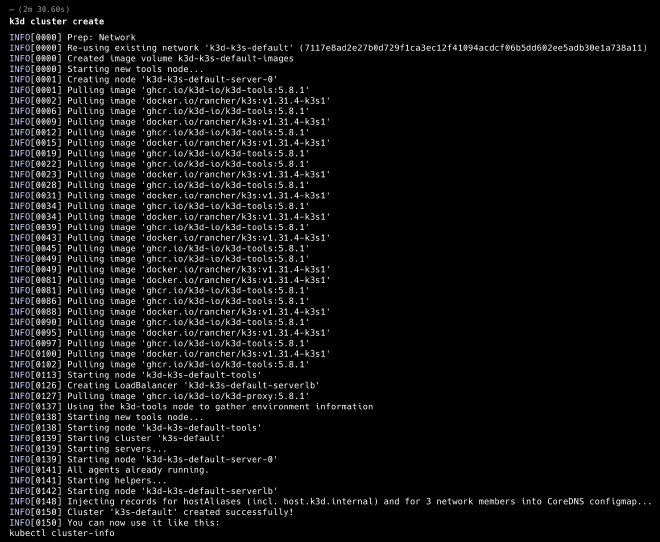
Access to Cluster#
As we mentioned before, many things are automatic in K3s, and the configuration to use it is not the exception since the context is updated in our .kubeconfig file. As soon as the installation is finished, we will be able to execute known commands in kubernetes and see that everything is working correctly, for example, we will see how many nodes and pods our cluster has:
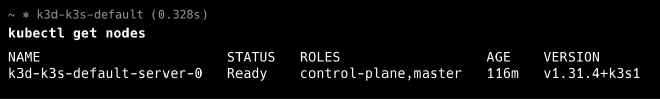
Nodes#
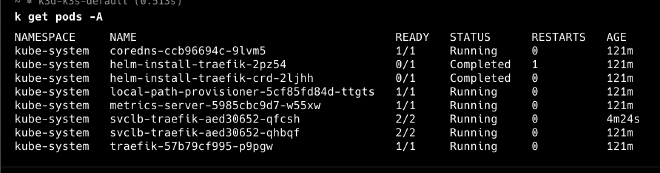
Pods#
And so far our introductory article, in a next article we will see how to add more nodes to the cluster for a more realistic environment, however, as you can see, K3S or K3D are a tool that facilitates the use of the technology either for specific use cases or when we do not want to explore in home labs without the need for monetary investment or be an expert in Kubernetes.
